Self-hosted Gitlab install guide
Intro
This is a pragmatic guide on how to install Gitlab on a self hosted server system. In this guide we will install gitlab-ee on the Ubuntu distro version 22.04, with nginx (there are options to use bundled or non-bundled nginx, see below).
For more information visit here.
Prepare the Environment
Install Postfix to send emails
During Postfix installation a configuration screen may appear. Select
Internet Siteand press enter. Use your server's external DNS formail nameand press enter. If additional screens appear, continue to press enter to accept the defaults.
Add Gitlab Package Repository and Installation
Add repository
Before continuing:
- Make sure the DNS is setup, (your DNS will be different but for the sake of this guide the DNS will be: "https://gitlab.example.com" ).
Gitlab Installation
Install basic command:
Or if you have your DNS setup you can add it in the installation, it can also be configured later.
You can also specify version:
After installing, besides the Gitlab server, you will also receive the gitlab-ctl maintanance CLI.
gitlab-ctl a Gitlab maintanance CLI
You use this to:
- reconfigure Gitlab
- see the current status of Gitlab services sudo gitlab-ctl status
- start Gitlab services
- stop Gitlab services
See more here.
[Option 1, tested] Configuring gitlab with non-bundled nginx
Install nginx
For more detailed info check here
See status
Handle SSL Certificates
Since we use non-bundled nginx we have to take care of the certificates.
If you already have certificates on the server you can skip the below content. I'm not sure how AWS handles this.
I use certbot and Let's encrypt to handle the certificate get and renewal process.
Configure Gitlab
You will find the configuration file at: /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
There you can configure gitlab values by following the documentation, here. Please go through it.
Here are quick values that are important to set (see docs):
external_url 'https://gitlab.domain.com'
web_server['external_users'] = ['www-data']
# Disable nginx
nginx['enable'] = false
# Disable lets encrypt
letsencrypt['enable'] = false
Run sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure for the change to take effect.
Configure nginx
Quick note on nginx
This is the nginx file structure:
You will use sites-available and sites-enabled directories.
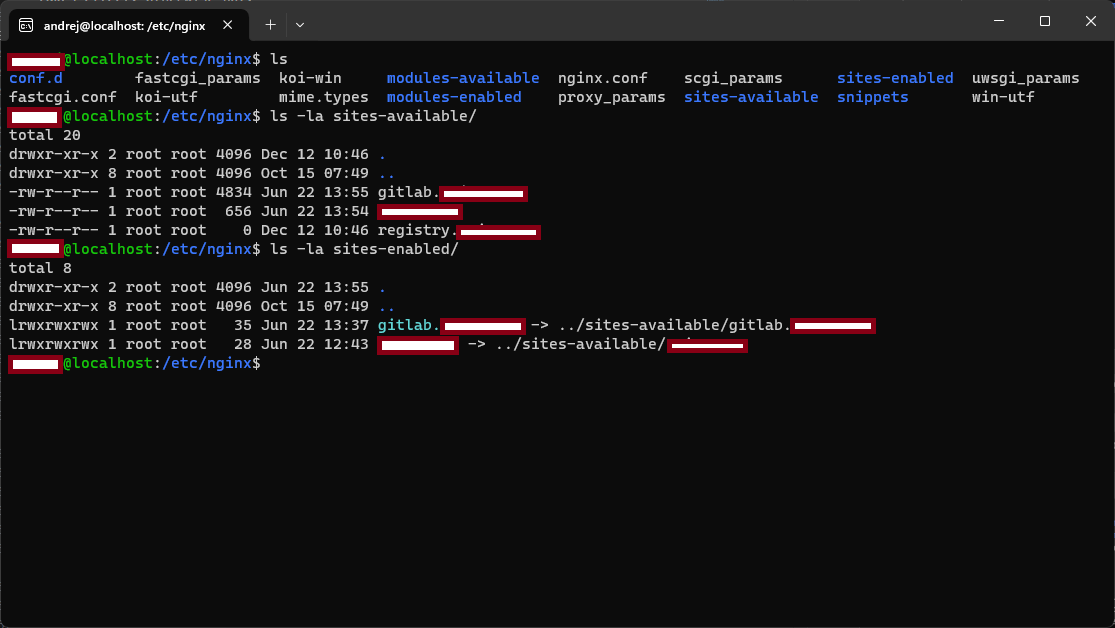
The actual configuration files will exist in sites-available and soft links to them in sites-enabled. If a soft link exists in sites-enabled the configuration takes effect, otherwise not.
You can hot reload the nginx when finished with configuration by:
service nginx reload
Configure with gitlab templates
You will find the nginx configuration templates here
Depending on what you want to do, select the template. Here is an example of the real-world working config nginx file gitlab.domain.com (it may be outdated).
## GitLab
##
## Modified from nginx http version
## Modified from http://blog.phusion.nl/2012/04/21/tutorial-setting-up-gitlab-on-debian-6/
## Modified from https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html
##
## Lines starting with two hashes (##) are comments with information.
## Lines starting with one hash (#) are configuration parameters that can be uncommented.
##
##################################
## CONTRIBUTING ##
##################################
##
## If you change this file in a Merge Request, please also create
## a Merge Request on https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/merge_requests
##
###################################
## configuration ##
###################################
##
## See installation.md#using-https for additional HTTPS configuration details.
upstream gitlab-workhorse {
# On GitLab versions before 13.5, the location is
# `/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse/socket`. Change the following line
# accordingly.
server unix:/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse/sockets/socket fail_timeout=0;
}
## Redirects all HTTP traffic to the HTTPS host
server {
## Either remove "default_server" from the listen line below,
## or delete the /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default file. This will cause gitlab
## to be served if you visit any address that your server responds to, eg.
## the ip address of the server (http://x.x.x.x/)
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name gitlab.domain.com; ## Replace this with something like gitlab.example.com
server_tokens off; ## Don't show the nginx version number, a security best practice
return 301 https://$http_host$request_uri;
access_log /var/log/nginx/gitlab_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/gitlab_error.log;
}
## HTTPS host
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name gitlab.domain.com; ## Replace this with something like gitlab.example.com
server_tokens off; ## Don't show the nginx version number, a security best practice
root /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public;
## Strong SSL Security
## https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html & https://cipherli.st/
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gitlab.domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gitlab.domain.com/privkey.pem;
# GitLab needs backwards compatible ciphers to retain compatibility with Java IDEs
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
## See app/controllers/application_controller.rb for headers set
## [Optional] Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security
## HSTS is a feature improving protection against MITM attacks
## For more information see: https://www.nginx.com/blog/http-strict-transport-security-hsts-and-nginx/
# add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains";
## [Optional] If your certficate has OCSP, enable OCSP stapling to reduce the overhead and latency of running SSL.
## Replace with your ssl_trusted_certificate. For more info see:
## - https://medium.com/devops-programming/4445f4862461
## - https://www.ruby-forum.com/topic/4419319
## - https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-configure-ocsp-stapling-on-apache-and-nginx
# ssl_stapling on;
# ssl_stapling_verify on;
# ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/stapling.trusted.crt;
# resolver 208.67.222.222 208.67.222.220 valid=300s; # Can change to your DNS resolver if desired
# resolver_timeout 5s;
## [Optional] Generate a stronger DHE parameter:
## sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 4096
##
# ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
## Individual nginx logs for this GitLab vhost
access_log /var/log/nginx/gitlab_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/gitlab_error.log;
location / {
client_max_body_size 0;
gzip off;
## https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlabhq/issues/694
## Some requests take more than 30 seconds.
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Ssl on;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://gitlab-workhorse;
}
}
[Option 2, not tested] Configuring gitlab with bundled nginx
Manage certificates
See here on how to manage SSL certificates.
Configure Gitlab
You will find the configuration file at: /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
Follow here on how to configure.
Login to Gitlab
Unless you provided a custom password during installation, a password will be randomly generated and stored for 24 hours in
/etc/gitlab/initial_root_password. Use this password with usernamerootto login.
Appendix (just for reference)
Set values from real world configuration at: /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:
## GitLab URL
##! URL on which GitLab will be reachable.
##! For more details on configuring external_url see:
##! https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#configuring-the-external-url-for-gitlab
##!
##! Note: During installation/upgrades, the value of the environment variable
##! EXTERNAL_URL will be used to populate/replace this value.
##! On AWS EC2 instances, we also attempt to fetch the public hostname/IP
##! address from AWS. For more details, see:
##! https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/instancedata-data-retrieval.html
external_url 'https://gitlab.domain.com'
external_url 'https://gitlab.domain.com'
gitlab_rails['initial_root_password'] = "som-init-pass"
web_server['external_users'] = ['www-data']
nginx['enable'] = false
Used commands from real world installation:
apt update
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install gitlab-ee
sudo nano /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
sudo gitlab-ctl status
systemctl restart nginx.service
systemctl status nginx.service
gitlab-ctl status
sudo gitlab-ctl status
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
ps -aux
ps -aux | grep pb
ps -aux | grep pocket
sudo gitlab-ctl tail puma
References
“Installing a GitLab POC on Amazon Web Services (AWS) | GitLab.” Accessed December 12, 2023. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/install/aws/. @InstallingGitLabPOC